Do Governments Ever Listen to ‘The Science,’ Or Do They Seek post hoc Fig Leaves?

The UK government has consistently argued that its approach to the COVID-19 epidemic follows the best scientific knowledge available. To the average person, it sounds reassuring. But it relies on the widespread belief that there is a correct scientific answer to a problem, and that governments simply need to be led by “the science.”
But as students of science policy know, scientific knowledge does not necessarily lead to a specific course of political action, let alone to the “best” policy. Scientific knowledge is often irrelevant to policy making, and policies are often based on knowledge that is cherry picked for political reasons.
“Being led by the science” evokes a linear model of policy making which is more a myth than reality. In reality, politicians use claims about scientific knowledge in order to justify a course of action.

Knowledge is political
COVID-19 is a threat to everyone, and any course of action will involve a significant number of people dying. Knowing that lives hinge on the outcome of decision making should compel governments to explain the conclusions of different sources of scientific evidence, and be open about how they reached policy decisions. This might involve reaching out to opposition parties, or organizing consultations with medical professionals and the public to hear their concerns.
Instead, the government most often decides what the “best available science” means, and tries to reassure rather than consult the public about the best way forward.
This attitude isn’t unique to the current UK government. As Sheila Jasanoff, professor of science and technology at Harvard University, said of the mad cow disease outbreak in 1996:
The response to radioactive contamination in the Cumbrian fells in 1986, shortly after the Chernobyl nuclear disaster, is another good example. The government referred to modelling of nuclear fallout to predict that it would soon be safe for sheep farmers to return their flocks to pasture. Then a ban was imposed on the movement and slaughter of sheep. Brian Wynne, a professor of science studies, noted, scientific reassurances were made that the ban would only last three weeks, but then the restrictions were imposed indefinitely. The result was massive loss in public trust.
Acting on ‘the science’
The government announced restrictions on social gatherings and announced a partial lockdown on March 24, after a slow build up during which pubs and restaurants remained open. The decision to change tack was allegedly based on a new study by researchers from Imperial College London, published on March 16, which warned that up to 510,000 people could die if no controls were introduced.
But the government’s own chief medical adviser, Chris Whitty, said on March 12 that worst-case scenario planning projected 80 percent of the country would contract the virus, with a 1 percent mortality rate. This equated to more than 500,000 deaths.
Taking professional and public concerns seriously, the government could have pointed out the main challenges the UK was facing. While there is still a great deal unknown about COVID-19, these challenges should have been clear from the outset.
We know that the growth of infections follows an exponential function where the doubling time of infection is between two and four days in the first weeks of the epidemic. The incubation period of COVID-19 is rather long, between five and 14 days, which is more than double that of the seasonal flu. This means the likelihood of transmitting the virus before having symptoms is much higher with COVID-19. While the true mortality rate is still unknown, it is assumed to be around 1 percent for those without underlying health problems. It is much higher otherwise, and it is much higher compared to the seasonal flu.
These three facts provide practical guidance for managing the epidemic. They call for restricting opportunities for exposure to the virus and ramping up the capacity of the healthcare system quickly. Acting sooner rather than later makes a big difference in the total number of infections and deaths.
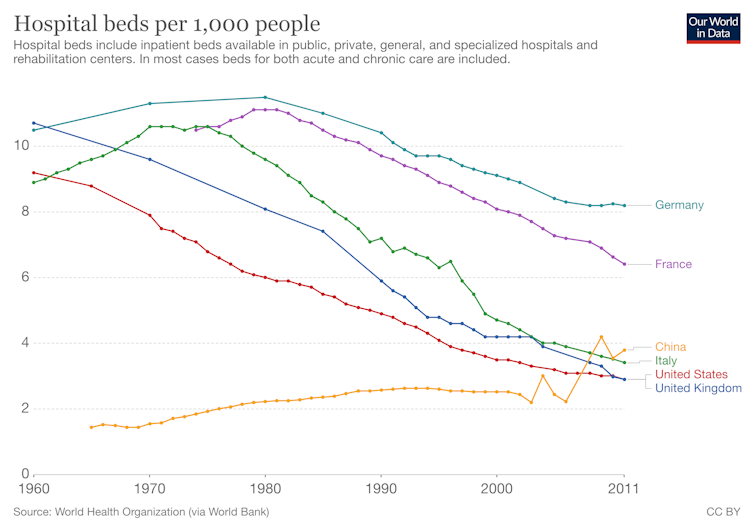
But as cases mount in the UK, there are nearly 100,000 vacancies for medical professionals in the NHS and the UK has one of the lowest numbers of hospital beds per 1,000 people. Personal protection gear for doctors and nurses is also lacking in many hospitals.
The UK government has benefited from the British tradition of standing together in a crisis, but it has also thwarted a much-needed critical examination of the government’s actions and pronouncements.
The government determines what knowledge is suitable for public consumption, and tries to develop and update a narrative based on reassurance, rather than transparency and trustworthiness. Precious time has been lost through this top-down approach to crisis management, excluding the public from an important debate.






















































































